Pressure ulcers, also called sores or bedsores, are a serious health problem. They are caused when skin or soft tissue is compressed between a bony prominence of the body and an external surface such as a bed or a wheelchair.
Initially it appears as a reddened area that may advance to the appearance of an open wound. These lesions can produce pain, tissue damage, and are difficult to heal, in addition to the high associated costs.
How do they develop?
The sick person, unlike a healthy person, mobilizes with difficulty or not at all, therefore there are areas of their body that remain compressed against the bed, armchair or wheelchair, thus reducing or suppressing the circulation.
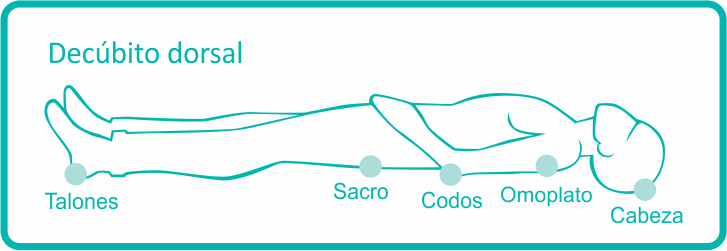
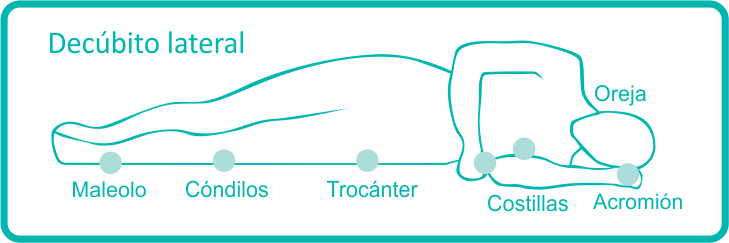
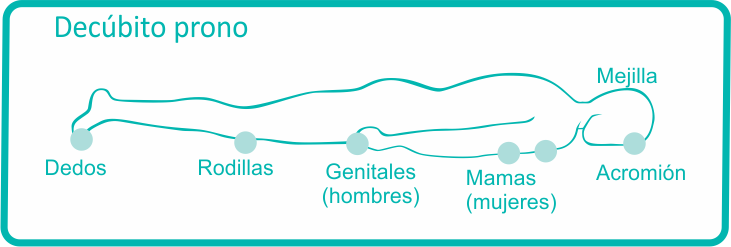
The areas that are most frequently affected are those where there are bones located very close to the skin, especially in shoulders, elbows, hips, tailbone and ankles.
Risk factors
- Advanced age. Seniors are at greater risk due to the changes of aging.
- Little mobilization. The lower level of activity and therefore of mobilization decreases the circulation.
- Poor nutrition. Protein-deficient diet promotes poor or no wound healing.
- Dehydration. Over hydration (edema) as well as dehydration makes healing difficult.
- Incontinence. Urine and stools produce skin irritation, which favors the destruction of the skin.
- Coexisting conditions. Such as paralysis, cancer, diabetes mellitus, among others
How are they prevented?
- Lowering the pressure
-
- Change positions frequently (recommended every 2 hours).
- Placing supportive devices to avoid and relieve pressure on the gluteal and coccyx region, such as a rolled blanket that is placed around the waist and thigh area. In the case of knees and ankles, it is recommended to use gloves with water between these areas.
- It is recommended to mobilize people, not to drag them.
- Skin Care
-
- Daily check.
- Keep skin clean and dry.
- If creams are applied, they must have a balanced (neutral) pH.
- TBe careful when massaging (gently).
- Keep good personal hygiene. In case the patient wears a diaper, please change it immediatly after use.
- Proper diet
-
- The diet should always contain, unless medically indicated, products rich in protein, as well as carbohydrates, fluid intake, fruits and vegetables.
- Keeping on the move
-
- Position changes.
- Roll the patient from side to side, as small changes in position will help improve blood circulation.
- If you are on a wheelchair for a long time, shift your weight frequently.
Warning signs
- A red area that does not go away.
- A blister, an open area, or a scratch.
- A black or bluish area.
Remember that the best treatment for bedsores is prevention.